Simulation of Pre processing for 3D printing
Pre-processing for 3D printing
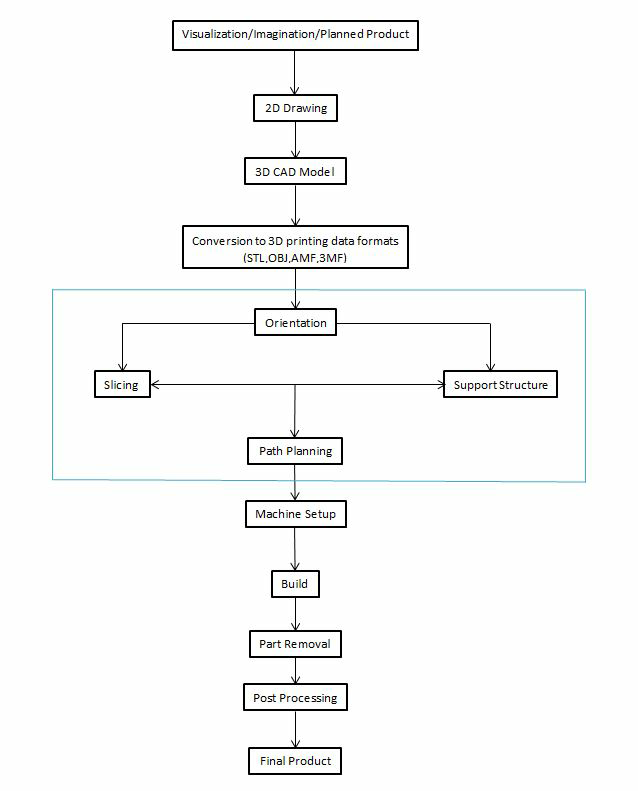
Pre-processing encompasses the steps between design and printing. Process of 3D printing starts with designing in CAD. Then printer software slices 3D CAD file into layers. For each slice, the software converts the data into machine code that determines tool paths for the machine to follow. The various steps in pre-processing from design to printing are as follows:
- CAD File
- Conversion to STL a. Orientation b. Support Structure c. Slicing d. Path Planning
1. CAD File
Every manufacturing process starts with the process of designing and as in any type of manufacturing, there are certain limitations to the materials and manufacturing processes that dictate how the product should to be designed, 3D printing is no different. In 3d printing, characteristic of hardware, software, temperature, filament and many other factors plays an important role in how digital model translates into a printed object. Some of them are design a strong base, grain direction, overhung, wall thickness, round corners and tolerances.
2. Conversion to STL
In order to check the interface of the object and make it reliable to 3d printers, conversion to STL file is required. It also facilitates other features like quick error check, bridging the gap between CAD platforms, exhibition purposes and 3D digitizer extension.
a. Orientation:
Orientation plays a vital role in the final product of 3d printing as it affects the part accuracy, manufacturing time, strength and surface finish. There are various orientation by which we can print the object such as vertically upward, vertically downward and in horizontal plane.
b. Support Structure:
Support structures are required where the objects are unable to get printed directly. Support structures help to guarantee the printability of a section during the 3D printing measure and also it can assist with forestalling part twisting, secure a section to the printing bed and guarantee that parts are joined to the fundamental body of the printed part.
c. Slicing:
The motive behind slicing a 3D model is to transform the model into guidelines for the 3D printer. To play out this errand, the slicing software isolates the item into numerous layers. It's classified "slicing" since it "slices" the 3D model to make numerous layers. After the layers have been made, the slicing software applies different qualities to every one of them.
d. Path Planning:
Path planning helps in to improve the printed surface quality, shape accuracy and infill distribution quality. There are various ways for path planning which can be used to print the objects which may affects the following factors in object like raster path, grid path, spiral path and zigzag path.